Instructions:Bambu Labs P1S FDM 3D Printer with Automatic Material System (AMS)
Want to learn more about 3D printing in general? Visit Instructions:FDM Printing

for all |
This page needs: Photo of spools to illustrate AMS problems (cardboard spool, nearly empty spool with fixed end, nearly empty spool with loose end) Loading AMS (John is working on this) |
Slicer[edit | edit source]
Bambu printers use Bambu Studio for slicing and most printer functions. You can monitor prints, look for models, and do very basic printing functions using the Bambu Handy smartphone app. If you wish to access North Forge's printers remotely (ie monitoring using Bambu Handy or Bambu Studio), you will need to get North Forge's user credentials from the 3D printing trainer.
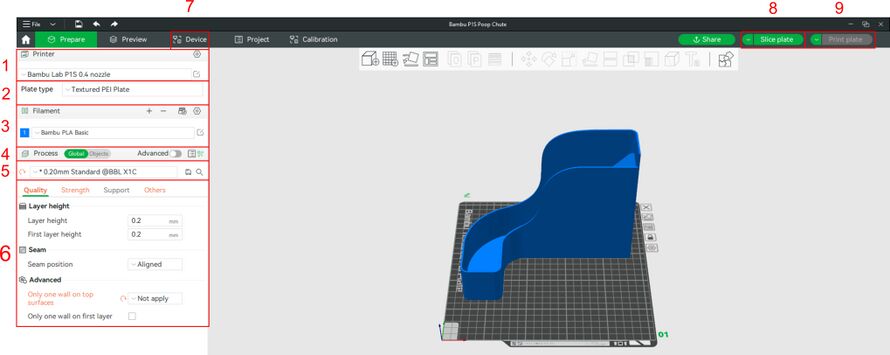
Overview[edit | edit source]
- Printer: This menu is used to select the printer type. Users will send prints to a specific machine at the end of the slicing process.
- Plate Type: This menu is used to select the plate type. Always ensure the plate type is suitable for the print and is physically installed on the printer.
- Material preset docker: This menu contains the types or colours of filament that will be used for the print job. Prints on the P1S standard printer will only have one option shown; when using the P1S with AMS, members can add more filament colours or types using the “+” button. Selecting the “edit” icon will open a list of available filament presets.
- Process: This menu is used to determine whether the selected options apply to the entire build plate or only to a single object. It also contains the layer height presets.
- Layer thickness presets: choose a preset for a given layer thickness.
- Slice Plate: This menu has standard printing options like infill, speed, temperature, and support.
- Device: this menu allows the user to monitor and control individual printers that are registered to the Bambu Studio account. This menu is automatically shown when a print is sent to a printer.
- Slice Plate: this option is used to slice the plate for printing. Users can also choose to slice a group of plates for consecutive printing using the drop-down menu (Slice All).
- Print plate: this option is used to send the plate to the printer and begin printing immediately. Users can also choose to only send the file to the printer but begin the print manually, or to export print files to portable media (MicroSD). Note: When printing directly from Bambu Studio, the print file is sent to Bambu’s foreign servers before being sent to the printer. Members with Intellectual Property concerns may therefore choose to export to portable media for printing.
Depending on the selected printer, different options may be displayed for the filament, calibration, and timelapse settings when the print is sent to a printer. Note that North Forge users have reported issues with print failures when using the timelapse setting.
General Workflow[edit | edit source]
- Select the printer type
- Select the build plate type
- Load the model
- Set model parameters: size, orientation, location on build plate
- Select the material(s) to be used in the materials docker. Assign colours if required.
- Select layer thickness
- Adjust material parameters as required. Typical parameters include infill (percentage and pattern), wall thickness (number of wall loops), support material, and skirt/brim.
- Slice the plate
- Send the plate to the printer
Sending to the Printer[edit | edit source]
Include warnings about "Print" vs "Send" and lack of options on-screen, issues with timelapse setting, instructions for assigning AMS bays, etc.
Material Load and Unload[edit | edit source]
Note that some filament spools will not work with the AMS. Cardboard spools, small spools, and nearly-empty spools that don't have the end secured to the core are not suitable. If you would like to use cardboard, you can try printing an adapter like this one (not tested or endorsed by North Forge).
The P1S with AMS can be loaded either through the AMS or through the normal back bay.
To load through the AMS:
- Open the AMS cover by twisting the locking lugs on either side.
- Place the spool on the rollers with the filament end coming forwards over the top of the spool.
- Press the grey loading button towards the back of the machine.
- Insert the filament into the loading hole until it is grabbed by the AMS.
- Wait for the AMS to automatically load the filament.
Poop Management[edit | edit source]
The Bambu P1S produces filament waste ("poop") that is ejected through a hole in the back. Accordingly, we have installed Poop Chutes to direct and collect the waste. Please empty the poop after each print.
As an experiment, North Forge is collecting ABS and PETG poop for recycling. There are two labelled buckets for poop. Please sort your poops into the appropriate bucket. The buckets are for poop and stringers only (not failed prints or other large clumps of waste).
Build Plates[edit | edit source]
The Bambu printers can use different build plates for different filament types.
When people handle the build plate, their hands will deposit oils and dirt that can affect the build plate. It's therefore a good idea to rinse the plate with soap and water periodically (every 3-4 prints) to remove oil and dirt.
Note that some build plates require a glue stick for proper adhesion; if you use a glue stick, please clean the plate with soap and water when you are done. Do not use isopropyl alcohol or solvents on the build plates.
Textured PEI Plate[edit | edit source]
The textured PEI plate is used for PLA, ABS, and PETG. It leaves a textured surface on the bottom of prints. Typically you will not need to use a glue stick, however if you're printing with PETG it can help protect the bed.
Engineering/Cool Plate[edit | edit source]
The engineering/cool plate is a double-sided plate. The cool side is designed specifically for PLA, though you can also use it for PETG. The engineering side is used for exotic engineering materials like ABS, TPU, PA, and Polycarbonate. Glue is strongly recommended for both the engineering side and the cool side.
Please also rinse the engineering/cool plate once you're done as glue buildup can affect other users' print quality. Use soap and water with a paper towel to remove glue build-up.
Useful Checklist[edit | edit source]
It's important that all printing parameters are consistent when printing. In particular, if you are downloading a pre-sliced file from Bambu MakerWorld, you should use this checklist to make sure they can be printed at North Forge.
- Correct printer type is selected (P1S or X1 Carbon - important for pre-sliced files)
- Correct build plate is selected, installed on the printer, and facing the correct direction (also important for pre-sliced files)
- Correct material profiles are selected in the project docker and assigned to the correct parts
- Supports and rafts are enabled if required
- If using the P1S with AMS, AMS option is checked when printing (even if using only one material)
- If this is unchecked, the printer will try to print via the back bay which is taken up by the AMS.
- AMS materials are assigned to the correct bay
- Build plate has been checked for completed prints, debris, and alignment before printing
Printing From Home[edit | edit source]
Printing from home is technically possible if you log in with North Forge credentials. However, there are several practical problems:
- You cannot always confirm that the correct filament and build plate are installed
- You may not be able to tell if there is an object on the print bed - the cameras cannot see the bed when it is fully loaded